Leading an Active Lifestyle with Degenerative Disc Disease
Category: Back Pain | Author: Stefano Sinicropi
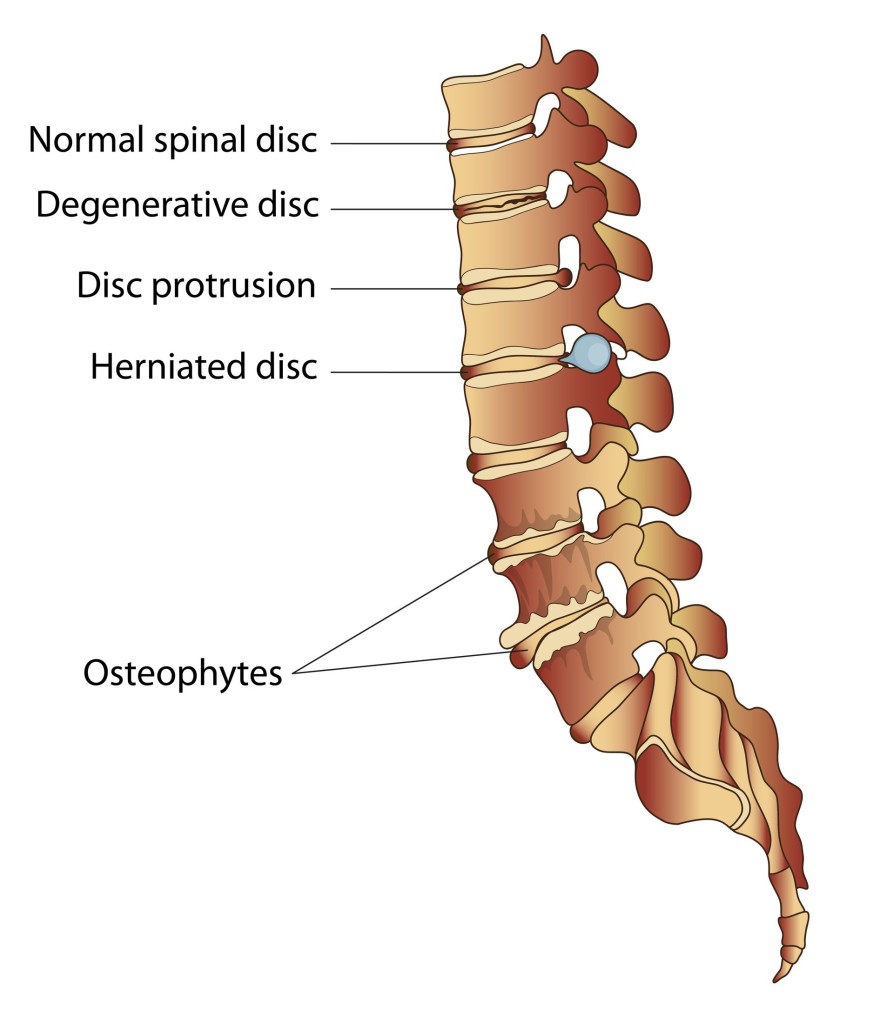 Degenerative disc disease refers to the typical degradation of the spinal discs as a person gets older (in this regard, it’s not actually a disease). This article will discuss what causes spinal discs to degenerate, and offer some tips on living an active lifestyle if you suffer from degenerative disc disease.
Degenerative disc disease refers to the typical degradation of the spinal discs as a person gets older (in this regard, it’s not actually a disease). This article will discuss what causes spinal discs to degenerate, and offer some tips on living an active lifestyle if you suffer from degenerative disc disease.
Degenerative Spinal Discs
The spinal discs degenerate as we get older, resulting in a loss of fluid as well as small cracks in the discs. This degrades the overall strength of the disc as well as its ability to absorb shock from the spinal vertebra. Degenerative discs are often associated with one or more of the following conditions:
- Osteoarthritis of the spine
- Herniated or bulging discs
- Stenosis of the spine
Every person’s body degrades over time – there is no escaping it. However, there are certain things you can do to slow down degenerative disc disease and continue to lead an active lifestyle if you suffer from back pain.
Tips for Leading an Active Lifestyle
Even if you suffer from degenerative discs, you need not be bedridden. Here are a number of ways you can still lead an active lifestyle if you suffer from degenerative disc disease:
- Exercise regularly. Remaining sedentary on the couch or at an office desk is actually bad for your spine. Getting up, going for a walk, or exercising in the gym will help combat degenerative discs, keep your spine mobile, and reduce back pain.
- Don’t ignore your pain. If you are experiencing back pain, pay attention to your body’s signals. Begin with conservative treatments like pain medications to combat the back pain. If those don’t work, see your doctor for additional options.
If you have been diagnosed with degenerative disc disease you have options for treatment. Talk to your physician about their recommendations for treatment. As we discussed in a previous post – you do not have to live with back pain. There are always treatment options, ranging from injections to surgery.